202301270201
Type :Example Tags : Category Theory
A Simple Example - cat theory 1
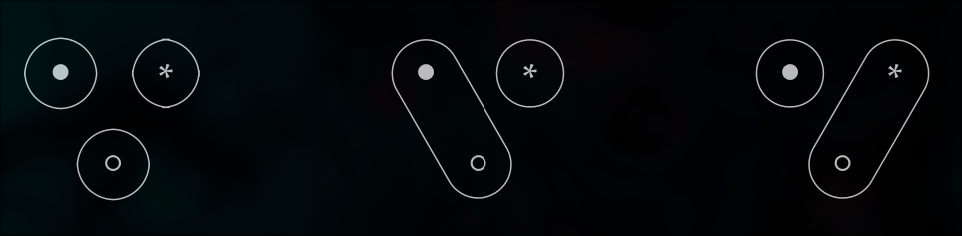
Consider three points; call them ●, ○ and ∗. Here the system: will simply be a way of connecting these points together. This connection can represent points as sites on a power grid, or a system describing connection by power lines. or as people susceptible to some disease, with a system describing interactions that lead to contagion.
An example of such a system would be like:
 The connections are symmetric and transitive so friendship cannot be represented by the system as a it is not transitive( A friends’ friend is not necessaritly a friend) but a disease or a possible communication can be.
Two more systems can be
The connections are symmetric and transitive so friendship cannot be represented by the system as a it is not transitive( A friends’ friend is not necessaritly a friend) but a disease or a possible communication can be.
Two more systems can be
 Now we define an observation , which is if ● is connected to ∗.
There are a total of systems and assigns
Now we define an observation , which is if ● is connected to ∗.
There are a total of systems and assigns true to the following systems
 and it assigns
and it assigns false to the remaining systems
The last part of the setup is the sort of operations that we want to perform on the system, one common example is called join. The idea being that the connectivity observations will not be compositional with respect to the join operator, which will be the generative effect.
The Join of two systems and is performed by combining their connection, denoted by
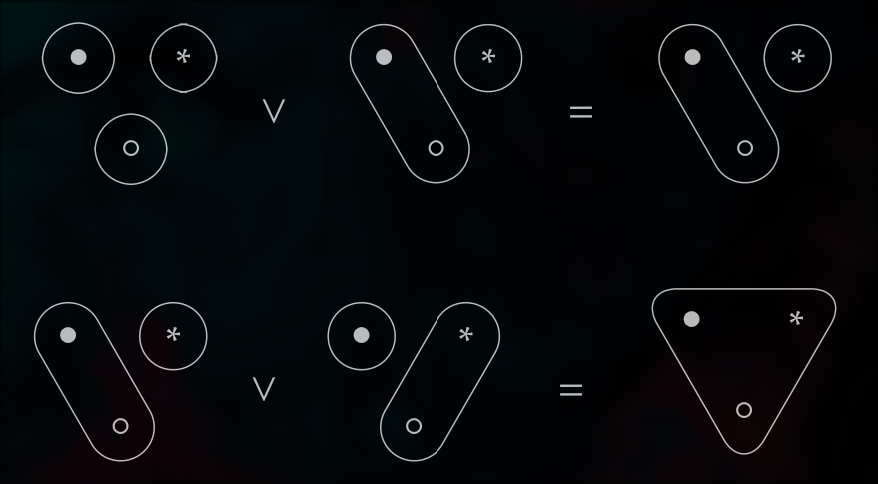 The last example joins two systems that are assigned
The last example joins two systems that are assigned false by the but their join is assigned true. Hence the observation is lossy under and a more detailed observation is needed which also inclued ○.